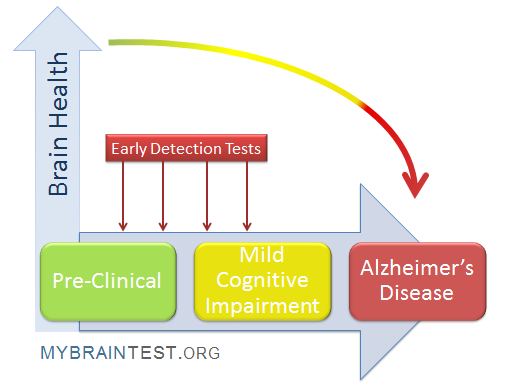
Early detection of Alzheimer’s is crucial for improving the quality of life for individuals at risk of developing this neurodegenerative disease. Recent advancements in cognitive impairment tests have revealed that the sense of smell may serve as an early warning sign for Alzheimer’s, helping to identify those in need of an Alzheimer’s risk assessment long before memory symptoms manifest. The innovative olfactory dysfunction tests developed by researchers allow participants to engage in a home-based Alzheimer test, making early diagnosis more accessible and less invasive. By recognizing cognitive decline through simple scent recognition, individuals can receive timely interventions, potentially altering the course of their disease. With ongoing research and implementation, these findings could revolutionize neurodegenerative disease detection and pave the way for more effective strategies in Alzheimer’s management.
Identifying warning signs of Alzheimer’s disease before clinical symptoms appear is an innovative area of research that is gaining traction. This proactive approach, often termed as cognitive evaluation, focuses on assessing individuals’ awareness and response to various stimuli, including scents. Studies have shown that changes in olfactory perception can be correlated with cognitive decline, highlighting the significance of olfactory tests as a potential non-invasive method for early diagnosis. By utilizing home-based assessments, individuals can conveniently evaluate their risk factors without the stress of clinical settings. As we delve deeper into this field, it’s crucial to explore additional methodologies that can complement early detection strategies for neurodegenerative disorders.
Understanding the Role of Olfactory Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Detection
Olfactory dysfunction is emerging as a critical sign in the early detection of neurodegenerative diseases, especially Alzheimer’s disease. Researchers have observed that a diminished sense of smell can precede cognitive impairment by several years. This connection indicates that olfactory testing could serve as a valuable cognitive impairment test, offering a simple, non-invasive method to assess individuals’ risk of developing Alzheimer’s. By recognizing these early signs, healthcare professionals can implement preventive measures proactively, allowing for better patient outcomes.
In fact, studies have demonstrated a significant correlation between odor memory tasks and cognitive performance. The olfactory test developed by researchers from Mass General Brigham focuses on the ability to discriminate, identify, and remember odors—a process closely tied to cognitive functions. This type of Alzheimer’s risk assessment is not only innovative but also highlights the necessity for continuous exploration into new methodologies for diagnosing neurodegenerative diseases.
At-Home Alzheimer’s Tests: A Revolutionary Approach to Early Detection
The development of at-home Alzheimer tests represents a groundbreaking shift in the approach to early diagnosis of cognitive decline. Using a simple card with odor labels, individuals can perform tests in the comfort of their homes, making cognitive screenings accessible to a broader audience. Research has shown that older adults who experience cognitive impairment tend to score lower on these olfactory tests compared to their cognitively intact peers. This indicates that home-based Alzheimer tests can be an effective tool for assessing cognitive health, thus enhancing early intervention strategies.
Implementing at-home tests can empower individuals and families to take charge of cognitive health management. By providing a straightforward method to evaluate one’s cognitive function, users may feel more inclined to seek further assessment and support if needed. Moreover, this testing approach alleviates barriers to access, allowing for a timely Alzheimer’s risk assessment that can potentially lead to early treatments and lifestyle adjustments. This paradigm shift places emphasis not only on advancing research but also on enhancing the quality of life for those at risk.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Research: Innovations in Diagnostic Tools
As research in Alzheimer’s detection progresses, innovative diagnostic tools such as olfactory tests hold significant promise. The integration of cognitive impairment assessments with olfactory evaluations offers a multi-faceted approach to understanding neurodegenerative diseases. Tools like the Aromha Brain Health Test are paving the way for more research into the relationship between smell and cognitive function. This type of research is crucial as it expands the toolbox available to clinicians seeking to assess Alzheimer’s risk more effectively.
Moreover, the potential for these olfactory tests to be used in various languages and demographics increases their applicability in diverse clinical settings. Such inclusivity ensures that cognitive impairment tests can reach a broader audience, ultimately leading to better health outcomes. The future of Alzheimer’s research stands on the brink of a transformation, with innovative techniques promising to change how we detect and understand this challenging neurodegenerative condition.
Olfactory Testing: A Game-Changer in Alzheimer’s Early Detection
Olfactory testing could significantly impact the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease due to its simplicity and effectiveness in evaluating cognitive functions. Given that the sense of smell is often one of the first cognitive abilities to decline with age, incorporating olfactory tests into standard Alzheimer’s risk assessment protocols may enhance diagnostic accuracy. This revolutionary approach leverages our understanding of neurobiology and olfactory pathways, promising to change how we perceive early cognitive impairment.
Furthermore, these tests provide a non-invasive, cost-effective alternative to conventional cognitive assessment methods. The ability for older adults to conduct these tests at home without medical supervision is a considerable advantage, removing the anxiety associated with clinical visits. Such innovations in Alzheimer’s detection hold the potential to not only facilitate timely interventions but also increase awareness and understanding of cognitive health among the general population.
The Link Between Age, Cognitive Decline, and Olfactory Ability
Research consistently indicates a strong correlation between age and declines in both cognitive function and olfactory ability. As individuals age, the likelihood of experiencing a decrease in their sense of smell increases, which can serve as an indicator of underlying cognitive issues. This connection highlights the importance of integrating olfactory dysfunction assessments into routine cognitive impairment tests, ultimately enabling earlier Alzheimer’s diagnosis and intervention.
The findings that older adults with mild cognitive impairment show diminished odor discrimination and identification reveal the urgency of addressing these indicators in clinical settings. Early intervention can be crucial in slowing disease progression, and recognizing the decline of olfactory abilities could prompt health care providers to initiate further Alzheimer’s risk assessment measures. Such steps are vital for improving longevity and quality of life in aging populations.
Innovative Approaches to Cognitive Health Management
Advancements in research also point towards innovative approaches in cognitive health management, emphasizing the importance of early detection strategies like olfactory testing. Utilizing these new methodologies not only allows for timely identification of potential neurodegenerative diseases but also encourages engagement in lifestyle modifications that can enhance cognitive health. Individuals identified through home-based tests may be motivated to participate in cognitive exercises and treatments that could slow the progression of Alzheimer’s symptoms.
This proactive management is essential as it fosters a culture of awareness around cognitive health. By prioritizing early detection, families and healthcare providers can implement strategies comprehensive enough to provide support and education, addressing both cognitive impairment and quality of life. Consequently, by embracing innovative tools, we can progress toward a future where the risks of Alzheimer’s disease can be significantly minimized through early detection and intervention.
The Significance of Multilingual Testing in Alzheimer’s Research
In our increasingly multicultural society, the development of multilingual cognitive assessment tools—such as olfactory tests—creates a significant opportunity for inclusion in Alzheimer’s research. The ability to conduct tests in both English and Spanish, as demonstrated in recent studies, ensures that linguistic barriers do not hinder access to critical cognitive health assessments. This is imperative as it ensures that findings are applicable across diverse populations, promoting a more comprehensive understanding of Alzheimer’s risk.
Moreover, multilingual testing enriches the research landscape by including a variety of perspectives and experiences related to cognitive health challenges. This inclusivity can lead to more tailored interventions that meet the needs of different communities, ultimately improving outcomes for individuals regardless of their primary language. As research continues to evolve, embracing diverse methodologies in Alzheimer’s testing will remain integral to advancing public health initiatives.
Challenges and Solutions in Early Alzheimer’s Detection
Despite the advancements in at-home testing and olfactory benchmarks, challenges remain in the widespread adoption of these early detection methods for Alzheimer’s disease. A significant barrier is the perception and awareness surrounding these cognitive impairment tests. Many individuals may be unaware of the importance of early diagnosis or may not recognize the subtle signs of olfactory dysfunction as significant warning signals. Efforts to educate the public on the relevance of such assessments can pave the way for increased participation in preventive health measures.
Additionally, it’s crucial to ensure that these innovative testing methods are integrated into health systems effectively. Collaborations between researchers, health care providers, and policymakers can facilitate the establishment of protocols that emphasize the importance of using at-home Alzheimer tests routinely. By addressing these challenges, we can establish a more robust framework for taking actionable steps in early Alzheimer’s detection and care.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Alzheimer’s Disease Research and Testing
As we look toward the future, it’s clear that ongoing research into Alzheimer’s disease will continue to evolve, embracing novel technologies and methodologies. The rise of olfactory tests stands as a testament to the innovative approaches that researchers are adopting to ensure early detection of cognitive decline. Future studies are expected to explore the integration of olfactory assessments with other cognitive impairment tests to formulate a more comprehensive risk profile for individuals.
Moreover, with an increased focus on neurodegenerative disease detection through innovative methods, we can anticipate more collaboration across disciplines, leading to a deeper understanding of Alzheimer’s pathology. This commitment to research will not only enhance our diagnostic capabilities but also create an environment where early interventions can effectively alter the course of the disease, improving quality of life for countless individuals at risk.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does early detection of Alzheimer’s impact treatment options?
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial as it allows for timely intervention and planning. Identifying cognitive impairment through methods like olfactory dysfunction tests can help initiate treatments that may slow disease progression. By assessing Alzheimer’s risk early, healthcare providers can provide tailored support, lifestyle changes, and potential clinical trials that could improve outcomes for patients.
What role does olfactory dysfunction play in early detection of Alzheimer’s?
Olfactory dysfunction has emerged as a significant indicator of early Alzheimer’s disease detection. Research indicates that individuals with impaired sense of smell often show cognitive decline before other symptoms arise. Tests that evaluate odor identification and memory can effectively assess Alzheimer’s risk, allowing for interventions before the onset of more pronounced memory loss.
Can at-home tests accurately assess Alzheimer’s risk?
Yes, at-home tests designed to evaluate olfactory function can provide a reliable assessment of Alzheimer’s risk. Studies have shown that older adults can successfully take these tests in a home setting. Early detection through such methods can identify cognitive impairment early on, facilitating timely medical consultations and possible treatment options.
What is the connection between cognitive impairment tests and Alzheimer’s risk assessment?
Cognitive impairment tests, including olfactory tests, play a vital role in Alzheimer’s risk assessment. These tests help identify subtle changes in memory and perception that may indicate early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. By focusing on these indicators, healthcare providers can better detect neurodegenerative diseases and implement proactive measures.
How effective are olfactory tests compared to traditional cognitive impairment tests?
Olfactory tests are increasingly recognized as effective tools for early detection of cognitive impairment compared to traditional tests. They are simple, noninvasive, and can often yield results quickly. Research has shown that adults with cognitive impairments tend to perform poorly in olfactory tests, which can complement traditional assessments and enhance overall Alzheimer’s risk evaluation.
What other neurodegenerative diseases can be detected through early cognitive tests?
In addition to Alzheimer’s disease, early cognitive tests, particularly those assessing olfactory function, may also indicate risks for other neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Identifying olfactory dysfunction can provide early warnings for these conditions, enabling early diagnostic measures and treatments.
What are the benefits of early detection of Alzheimer’s through home-based tests?
Home-based tests for early detection of Alzheimer’s offer numerous benefits, including convenience, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness. These tests empower individuals to assess their cognitive health privately and trigger earlier medical consultations. Early detection allows for monitoring progress and initiating preventive strategies or treatments that may delay the onset of severe symptoms.
How can olfactory dysfunction serve as a predictive marker for Alzheimer’s?
Olfactory dysfunction can serve as a predictive marker for Alzheimer’s disease as it reflects subtle changes in brain function before cognitive symptoms appear. Research has shown that older adults who struggle with odor identification may be at a higher risk for developing Alzheimer’s. As such, olfactory assessments can be integrated into routine Alzheimer’s risk assessments for more proactive healthcare.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| At-Home Olfactory Test | A new test developed by researchers to assess smells at home for early detection of Alzheimer’s. |
| Cognitive Impairment and Smell | Older adults with cognitive impairment scored lower on smell tests compared to cognitively normal peers. |
| Demographic Inclusivity | The test was effective for both English- and Spanish-speaking participants. |
| Potential for Future Research | Future studies may combine olfactory tests with neuropsychological tests to predict cognitive decline. |
| Noninvasive and Cost-Effective | The goal is to provide a test that is accessible and easy to perform at home. |
Summary
Early detection of Alzheimer’s is crucial for managing the progression of the disease. The development of an at-home olfactory test shows significant promise in identifying individuals at risk before the onset of memory symptoms. This innovative approach not only allows for early intervention but also opens avenues for further research into neurodegenerative diseases, highlighting the importance of maintaining cognitive health in older adults. With continued advancements in testing methods, the potential for better outcomes in Alzheimer’s treatment is becoming increasingly attainable.