**Is sugar addictive?** This intriguing question has sparked significant debate among health professionals and nutrition researchers alike. While sugar certainly contributes to cravings and can lead to compulsive eating habits, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction like substances such as alcohol or nicotine. Nevertheless, the health effects of sugar, especially from processed foods laden with added sugars, are a growing concern in today’s society. As more individuals become aware of sugar addiction and its implications, understanding added sugar recommendations becomes essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Balancing our desire for sweetness while managing intake is key to avoiding the pitfalls of sugar cravings.
The issue of sugar’s potential to cause dependency has become more prominent as we examine our diets filled with sweeteners and processed products. Many people seek answers regarding the consequences of excessive sugar intake on their health and well-being. Terms like sweet substance dependency and refined sugar effects are now at the forefront of nutritional discussions. Experts are focusing on the implications of sugar-laden foods and the physiological responses that accompany high consumption rates. Within this context, exploring the health ramifications of our dietary choices is more crucial than ever.
Understanding Sugar Addiction: Is Sugar Addictive?
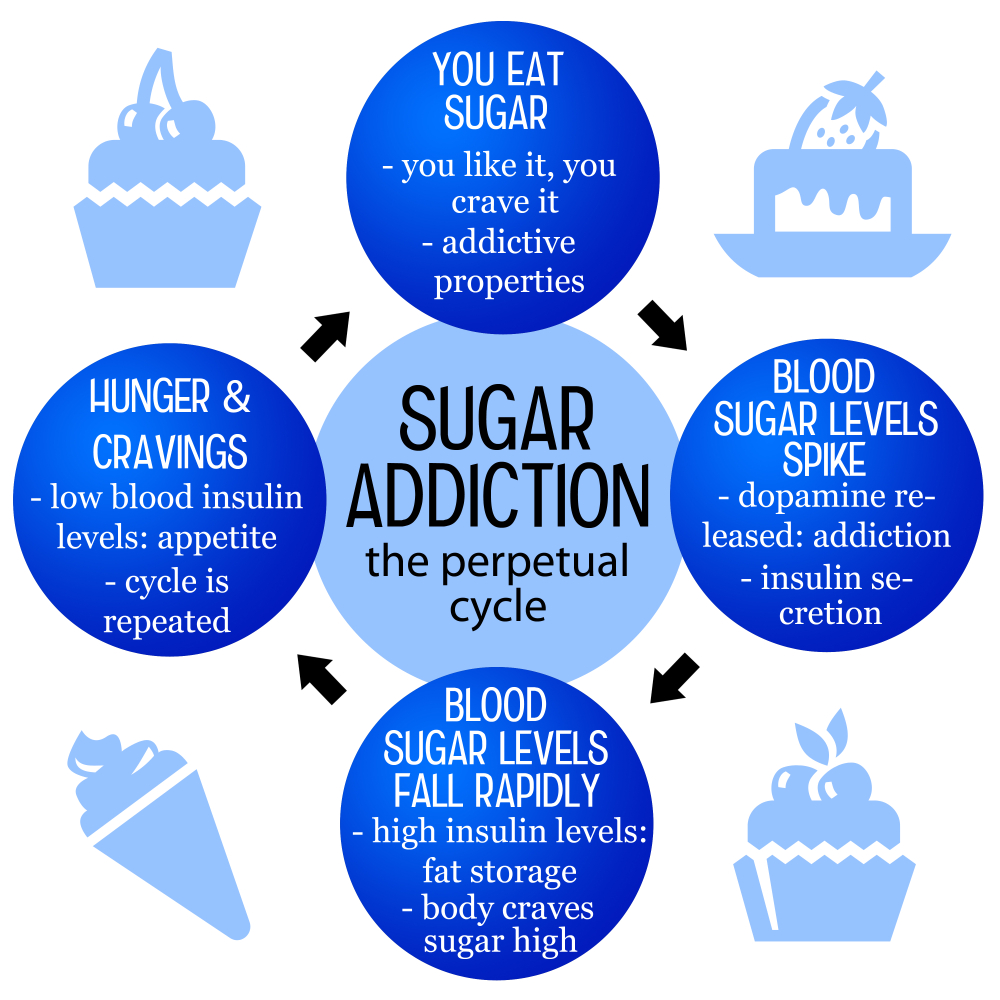
The debate surrounding sugar and its addictive properties often leads to many misconceptions. While sugar may trigger cravings and compulsive eating, which can resemble the behaviors associated with addiction to substances like alcohol and nicotine, it is vital to note that sugar does not meet the clinical criteria established for addiction. Experts, including nutrition researchers, suggest that while sugar can create habitual patterns of consumption, these patterns stem more from psychological conditioning and environmental factors than from a neurochemical dependency typically seen with addictive drugs.
Further complicating the matter, our modern food environment is inundated with processed foods laden with added sugars. This prevalence not only enhances cravings but also makes it easier for individuals to indulge in these high-sugar products frequently. People often experience withdrawal-like symptoms—such as irritability or intense cravings—when they attempt to cut back on these sugary foods, which adds to the perception of sugar as an addictive substance. Although such experiences can feel similar to those associated with traditional addiction, the underlying mechanisms and severity of symptoms diverge significantly.
Health Effects of Sugar: The Impact on Your Body
Recent studies have highlighted several health effects of sugar, particularly from excessive consumption of added sugars found in many of today’s processed foods. High sugar intake is linked to various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The average American consumes about 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, exceeding recommendations proposed by health authorities such as the American Heart Association. This excess not only contributes to weight gain but also influences metabolic health, leading to conditions such as insulin resistance, which can escalate into serious lifelong diseases.
Moreover, the impact of sugar on mental health cannot be overlooked. Research indicates that high sugar diets may contribute to mood swings and increased anxiety levels. The consumption of sugary foods can produce a temporary spike in energy and happiness, followed by a significant slump, often leading to further cravings for sugar and creating a vicious cycle of emotional eating. Therefore, awareness of the health effects of sugar is vital in promoting better dietary choices and healthier lifestyles.
Navigating Sugar Cravings: Recognizing and Managing Your Needs
Sugar cravings can be particularly challenging, as they often arise unexpectedly and can overwhelm one’s resolve to maintain a healthy diet. These cravings may intensify due to various factors such as emotional stress, lack of sleep, or even the habitual consumption of sugary foods. Understanding the psychological triggers behind these cravings is essential for developing strategies to combat them effectively. Instead of cutting sugar entirely, experts recommend a balanced approach that reduces sugar intake gradually, making it easier for individuals to adjust without feeling deprived.
One effective method to manage sugar cravings is through meal planning and preparation. Incorporating a variety of whole, nutrient-dense foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels and decrease the likelihood of sudden cravings for sweets. High-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, not only contribute to satiety but can also provide natural sweetness without the adverse effects associated with high levels of added sugar. Additionally, staying hydrated and ensuring adequate protein intake throughout the day can play a crucial role in managing cravings and improving overall health.
Processed Foods and Sugar: The Hidden Danger of Added Sugars
The omnipresence of processed foods in our diets often conceals the significant quantities of added sugar they contain. Many people unknowingly consume high levels of sugar due to the misleading labeling of these products, which can make it difficult to identify where high sugar content lurks. These processed foods are engineered to be palatable, leading to habitual consumption and an increased likelihood of sugar addiction-like behaviors—consuming more than intended, especially when these foods are readily available.
To combat the risks associated with high sugar intake from processed foods, consumers should develop the habit of reading food labels meticulously. Understanding the different names sugar can come under—such as high-fructose corn syrup, cane sugar, and more—is essential for making informed dietary choices. The awareness of how much hidden sugar is present in processed foods can empower individuals to reduce their consumption effectively and opt for healthier, whole food alternatives.
Added Sugar Recommendations: Establishing Healthy Limits
Establishing healthy limits for added sugar intake is crucial for promoting overall health and well-being. Leading health organizations recommend that men limit their intake to no more than 9 teaspoons per day, while women should aim for about 6 teaspoons, and even less for children. These guidelines are designed to protect individuals from the adverse health effects associated with excessive sugar consumption. Adhering to these recommendations can significantly reduce the risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases.
To achieve these recommended limits, individuals should be proactive in their dietary choices. Opting for natural sources of sweetness, such as fruits, can satisfy cravings without the detrimental effects linked with added sugars. It is also beneficial to gradually substitute high-sugar snacks and beverages with healthier alternatives, contributing to a more balanced and nutritious diet. This approach not only promotes health but encourages a sustainable relationship with food, reducing dependence on overly sweet products prevalent in our diets.
The Role of Sugar in a Balanced Diet: A Delicate Balance
Sugar can play a legitimate role in a balanced diet; however, the key lies in moderation. Carbohydrates, including sugars, are the body’s primary source of energy, and some naturally occurring sugars found in fruits and vegetables provide essential nutrients along with their sweetness. Understanding the difference between naturally occurring sugars and added sugars helps individuals make better dietary choices. While quick sources of energy can enhance a diet, excessive intake of added sugars can have adverse health consequences.
Thus, striking a balance is crucial. People can enjoy sweet treats in moderation while focusing on a diet rich in whole foods that provide broader nutritional benefits. Incorporating natural sources of sweetness and being mindful of portion sizes can allow for enjoyment without compromising health. Establishing this balance can lead to a more sustainable dietary pattern that accommodates occasional indulgences while prioritizing overall health and wellness.
Sugar Substitutes: Healthier Alternatives to Added Sugar
As concerns about sugar intake continue to rise, many are turning to sugar substitutes as a means to satisfy sweet cravings without the health risks associated with added sugars. These alternatives, such as stevia, monk fruit, and erythritol, offer sweet flavors with fewer calories and a lower impact on blood sugar levels. Incorporating these substitutes into recipes can help reduce the overall sugar content of diets, making it easier for individuals to adhere to recommended limits concerning added sugars.
However, it’s essential to approach sugar substitutes with caution. While they can be helpful in reducing sugar intake, some substitutes can produce unpleasant aftertastes or lead to digestive issues if consumed in large quantities. Gaining a better understanding of the different types of substitutes available, along with their potential health impacts, can help consumers make informed choices. Ultimately, the goal should be to find a balance of naturally sweet foods and appropriate use of substitutes, supporting both health objectives and personal preferences.
Mindful Eating: Strategies to Curb Sugar Consumption
Mindful eating is an effective strategy for managing sugar consumption and enhancing the overall eating experience. By focusing on the act of eating and recognizing hunger and fullness cues, individuals can cultivate a more honest relationship with food. Implementing mindful practices, such as slowing down during meals and savoring the flavors of food, can reduce the urge to reach for sugary snacks out of habit or boredom. This approach encourages deeper awareness of eating habits and can act as a countermeasure to sugar cravings.
Incorporating mindfulness into daily routines can also extend to meal planning and preparation. Preparing meals and snacks at home not only provides greater control over added sugar consumption but also promotes healthier choices by emphasizing whole food ingredients. Over time, the practice of mindful eating can lead to lasting changes in dietary patterns, fostering a holistic approach to nutrition that prioritizes well-being and satisfaction.
Breaking the Cycle: Overcoming Sugar Dependence
Overcoming a dependence on sugar often requires acknowledging the powerful hold that sugar can have on our cravings and eating behaviors. For many, the journey to reduce added sugar consumption can seem daunting, especially when faced with the temptations of highly palatable processed foods. Recognizing that it’s normal to experience cravings and withdrawal-like symptoms is a critical first step in this process. Strategies such as setting realistic goals for tapering off sugar, identifying and addressing triggers, and seeking support from friends or health professionals can empower individuals to break free from excessive sugar consumption.
Moreover, creating a supportive environment significantly aids in overcoming sugar dependence. This can involve removing processed sugary foods from the home or replacing them with wholesome options that nourish the body. As individuals discover alternative snacks and treats that satisfy their sweet tooth without the negative health impacts, they can gradually rewire their cravings. Establishing new habits takes time; hence, patience and perseverance are essential to breaking the cycle of sugar dependence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar does not fall under the clinical definition of an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, it can trigger cravings and compulsive eating behaviors. The palatability of sugar, especially in ultra-processed foods, can contribute to habitual consumption and withdrawal-like symptoms when intake is reduced.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Sugar addiction can lead to negative health effects such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. The overconsumption of added sugars, especially from processed foods, is linked to these health risks. Moderation is key, as excessive sugar intake can lead to serious health implications.
How do sugar cravings develop?
Sugar cravings develop due to the consumption of highly palatable foods that contain added sugars. These foods can trigger the brain’s reward system, leading to habitual eating patterns and heightened cravings. Reducing intake gradually can help manage these cravings over time.
What role do processed foods play in sugar addiction?
Processed foods are often high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, all of which can enhance cravings and lead to overconsumption. These foods are designed to be highly palatable and accessible, making them difficult to resist and contributing to habitual sugar intake.
What are the recommendations for added sugar intake?
The American Heart Association recommends no more than 9 teaspoons of added sugar per day for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and less for children. Monitoring your sugar intake is essential for maintaining health and preventing the adverse effects associated with sugar addiction.
Can people overcome sugar addiction?
Yes, individuals can overcome sugar addiction by gradually reducing their sugar intake. Instead of going cold turkey, monitoring consumption, reading food labels, and opting for natural sources of sweetness can help manage and reduce cravings over time.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Definition of Sugar Addiction | Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, despite increased cravings. |
| Cravings and Consumption | Ultra-processed foods high in sugar may lead to habitual consumption and withdrawal-like symptoms when stopped. |
| Dietary Recommendations | Moderation is key; the American Heart Association recommends limited daily sugar intake. |
| Sugar in Foods | Sugar naturally occurs in fruits, vegetables, and dairy, making it a necessary part of some diets. |
| Conclusion on Sugar Addiction | Sugar has some addictive qualities, but it is essential for enjoyment and can be consumed in moderation. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This topic has sparked widespread debate among nutrition experts, particularly regarding its classification as an addictive substance. While sugar can provoke cravings and emotional responses, it is crucial to understand that it does not meet the clinical criteria for addiction like alcohol or nicotine. Instead, sugar plays an essential role in many natural foods and can be enjoyed in moderation. By being mindful of our sugar intake and making gradual changes to our diets, we can enjoy sweetness without the adverse effects often associated with addiction.